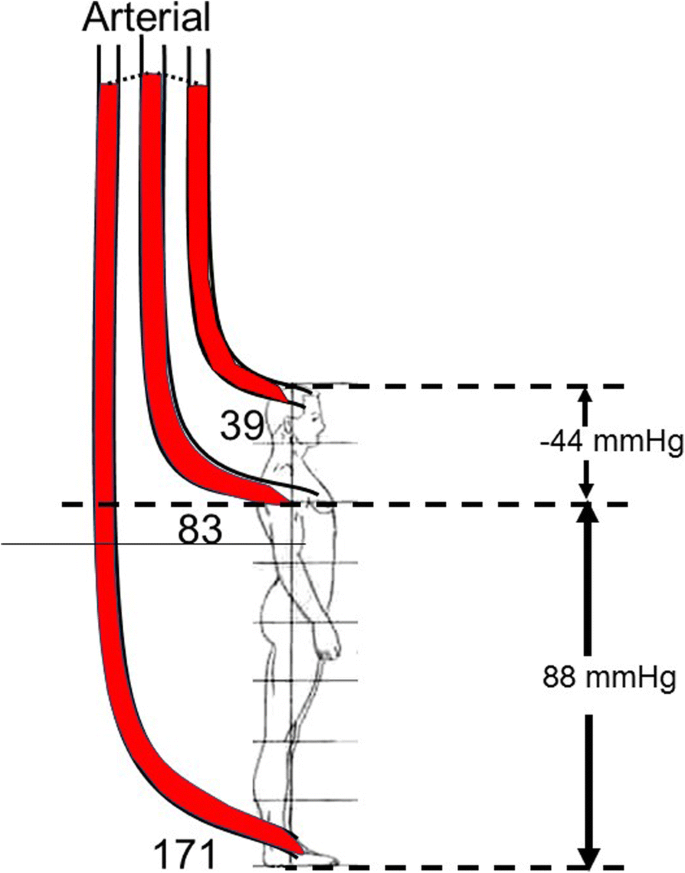
In many body regions the pressure within the veins can be increased by the contraction of the surrounding skeletal muscle. How is blood pressure measured.

Circulatory Systems
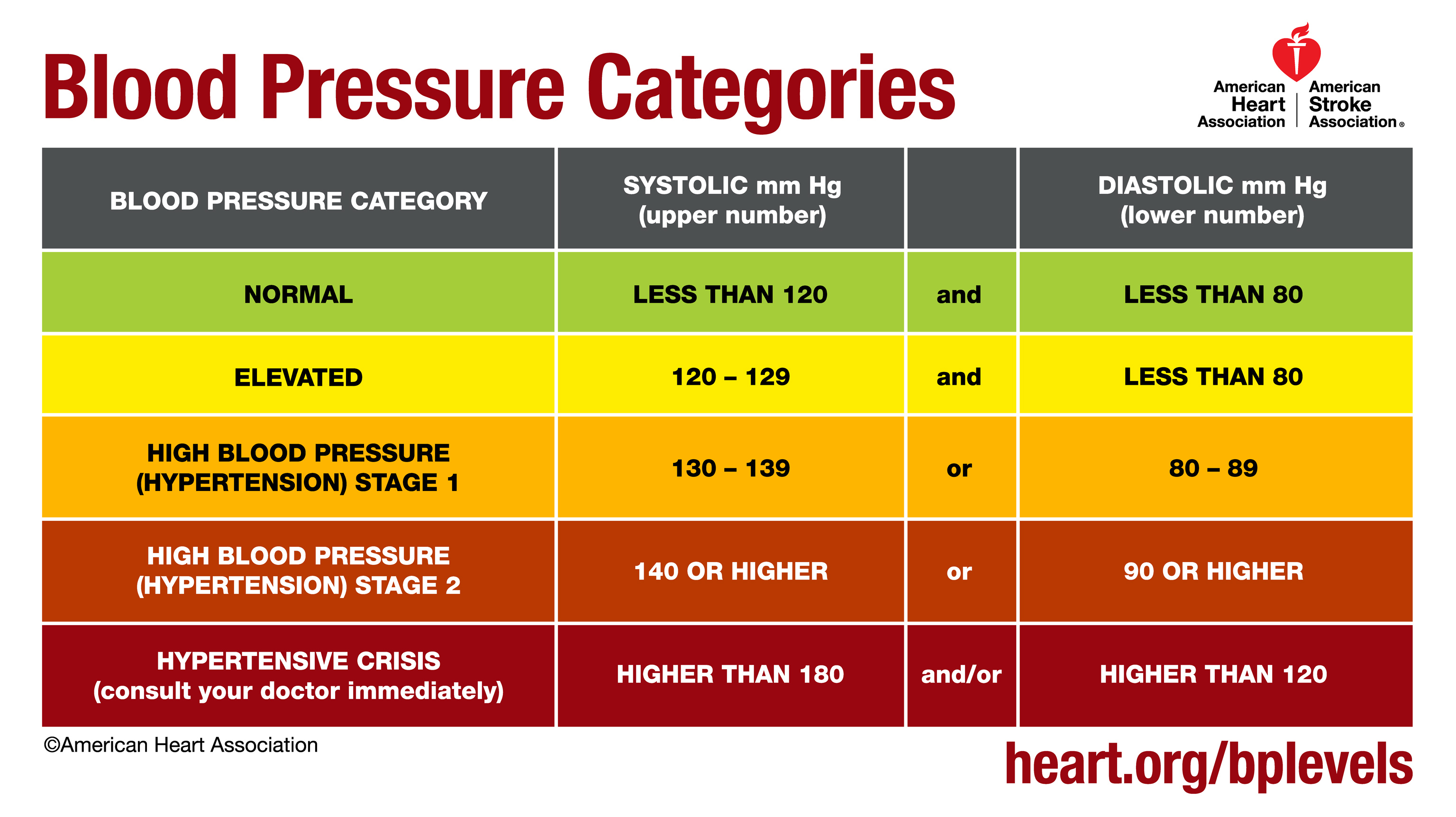
Measurement of the force of blood moving around the body. Blood pressure is measured in millimetres of mercury mmhg and is given as 2 figures. The most powerful is the left ventricle. Further they tend to flow more down the middle of the tube reducing friction with the tube wall. Diastolic pressure the pressure when your heart rests. Blood pressure is a measurement of the force on the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. You can measure your blood pressure at home.
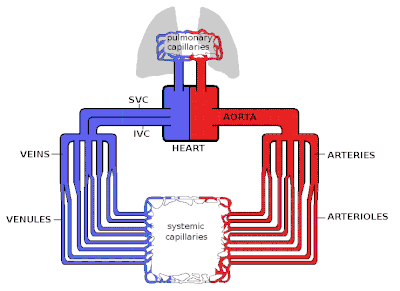
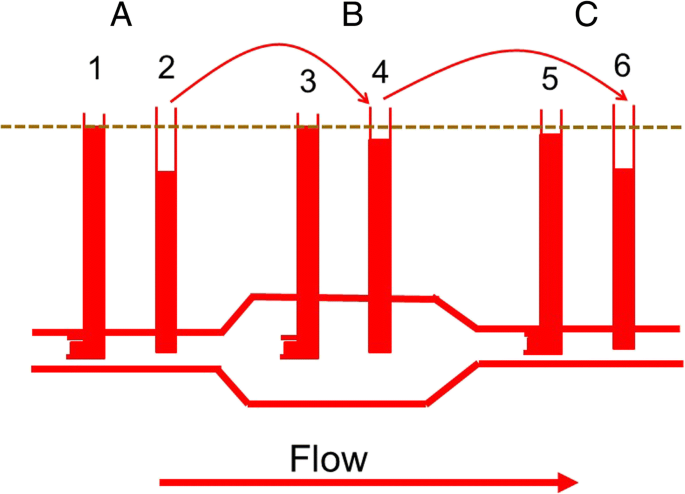
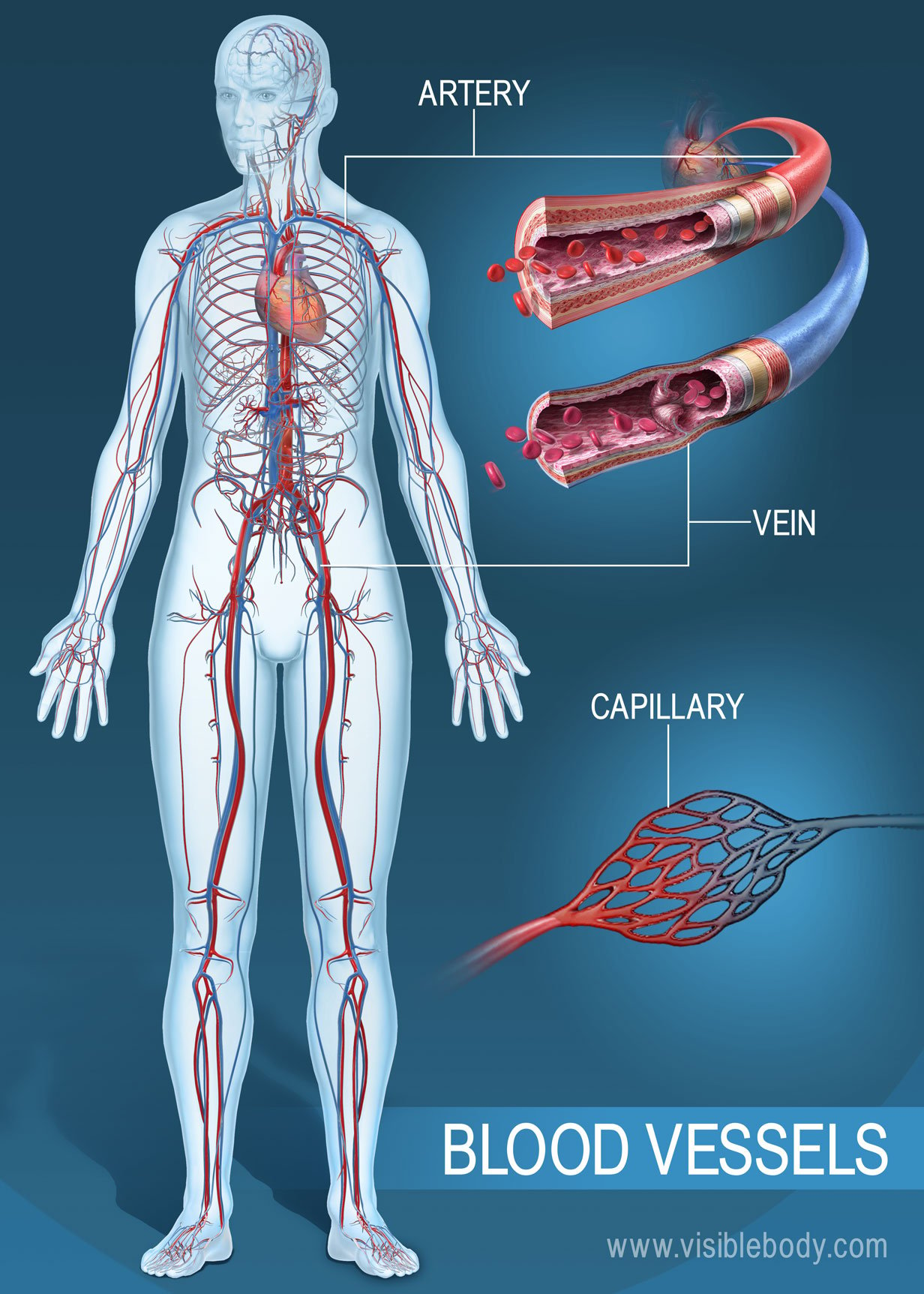
This mechanism known as the skeletal muscle pump figure 6 helps the lower pressure veins counteract the force of gravity increasing pressure to move blood back to the heart. It is there where blood delivers oxygen to the bodys cells. Ventricular contraction ejects blood into the major arteries resulting in flow from regions of higher pressure to regions of lower pressure as blood encounters smaller arteries. It is initiated by the contraction of the ventricles of the heart. Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flowthe circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systemsthe haemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Blood pressure is a measure of the force that your heart uses to pump blood around your body.
You can also have it checked at your health care providers office or even a fire station. This mechanism known as the skeletal muscle pump figure 2026 helps the lower pressure veins counteract the force of gravity increasing pressure to move blood back to the heart. Blood flow refers to the movement of blood through a vessel tissue or organ and is usually expressed in terms of volume of blood per unit of time. If the blood coming. Doctors measure your blood pressure as a way of quantifying the force being exerted by this moving blood against the walls of your arteries. The researchers claim that the effect comes from the red blood cells clumping together mostly in a line like box cars on a train.
Systolic pressure the pressure when your heart pushes blood out. The cells moving together as a train produces less resistance than if they were all bouncing around separately. When the heart beats it creates blood pressure during the ventricle contraction that move blood throughout the body. Thus haemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Because the heart beats the blood flow through the arteries is not steady as with a fire hose but pulsatile and the flow of blood and the pressure it exerts fluctuate from moment to moment. As leg muscles contract for example during walking or running they exert pressure on nearby veins with their numerous one way valves.
This oxygen rich blood then returns to the heart in the lower left portion or left atrium and exits through the upper portion or left ventriclethe blood moves through the body from that point through miles of blood vessels and arteries in order to move the oxygen into smaller pathways called capillaries.