If the tracer is metabolised a series of measurements can be made and assuming exponential decline first order kinetics the volume of distribution can be determined by extrapolation back to zero time. With the availability of rapid accurate assays the measurement of antibiotic material in serum and other body fluids is feasible desirable and widely practiced for these purposes.

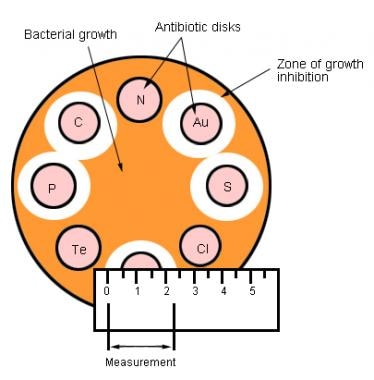
Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
Measurement of antimicrobial agents levels in body fluids. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents haroldj. For the other body fluids listed the subjects were generally hospitalized patients table 2. These studies suggest that the level of antimicrobial drug in sputum and bronchial secretions is of clinical impor tance. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobial agents is important when the margin between therapeutic and toxic levels is narrow. 4efficacy or toxicity is delayed or difficult to measure 5accurate assay is available. Antimicrobial levels and renal function for most antimicrobial agents renal excretion is the major pathway for elimination from the.
Laboratory tests that are usually considered helpful in guiding antimicrobial therapy include antimicrobial agent susceptibility tests determination of bacterial production of beta lactamase and assay of specific antimicrobial levels in serum and other body fluids. Pmc free article georgopoulos a. Not interfere with body fluid distribution if the tracer is excreted in the urine then the loss can be determined and corrections made in the calculation. A simple micro agar diffusion method for the determination of antibiotic concentrations in blood and other body fluids. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids biological assys immunoassays. Chisholm gd waterworth pm calnan js garrod lp.
Production greatly increased after. The values given for serum and urine were obtained from normal adults in controlled phar macologic studies table 1. The measurement of antibiotic concentrations in various fluids has been a prominent aspect of the evaluation of new antibiotics and the quality control of their manufacture. Most distribute well into various body fluids do not distribute well into csf unless meninges are inflamed. Concentration of antibacterial agents in interstitial tissue fluid. Constitutive inducible produced at low level wo stimulus.
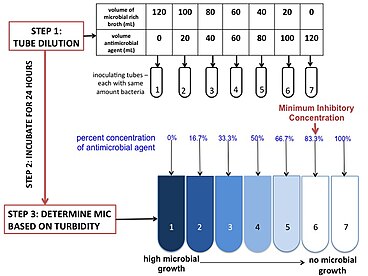
Poor clinical response being correlated with levels lower than the mic of the specific pathogen 12 15. Levels correlated with a statistically significant improvement in clinical outcome and a lower mortality. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids. Persistent suppression of bacterial growth after limited exposure to an antimicrobial agent 1. In contrast dilution methods allow determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration of an agent which can be correlated with blood urine and other body fluid levels of the antimicrobial agent. Jong yin department ofcommunity medicine schoolofmedicine university ofcalifornia sandiego lajolla california 92037 received for publication 10november 1969 apreviously described agar diffusion technique for microbioassay ofantimicro.